What Does It Mean to Be “In Our Senses”?
“Have you lost your sense?” This is a dialogue that we have all heard at one or another point in our lives.
But what does being in our senses mean?
The human body has five distinct senses: sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. Below is a brief explanation of the mechanics of our five senses:
The Five Senses Explained
Sight: When the neurotransmitters or receptors in the eyes react to stimuli like light and help the brain form visual images.
Hearing: When the inner ear receptors translate stimuli presented as sounds.
Smell: When the receptors in the nose detect chemicals like fragrances, odors, or aromas.
Touch: When the receptors in the skin collect information about textures, temperature, and pressure of an object and transmit this information to the brain.
Taste: When the receptors on the tongue react to chemicals in flavors — sweet, sour, bitter, or bland.
Are Senses a Learned Skill or an Inherited Phenomenon?
The five senses are not learned skills, but are natural abilities present in the human body at birth. However, not all five senses are fully developed from day one. For example, a newborn may have a developed sense of smell and taste, but their vision is limited.
At birth, children primarily rely on reflexes and are startled by sudden stimuli like loud noises or movement. As they grow, the senses develop — for example, sight typically takes 7–9 months to fully mature.
Different early learning philosophies approach this developmental timeline in unique ways. You can learn more in our article comparing Montessori vs Waldorf educational methods.
🌟 Support Sensory Development with the Right Tools
Sensory skills develop naturally, but hands-on Montessori materials accelerate learning by engaging multiple senses simultaneously. Our customers report noticeable improvements in focus, coordination, and exploration within weeks.
Development of the Senses in Early Childhood
Before diving into each individual sense, here’s a quick overview of typical sensory milestones by age:
| Age | Sensory Development |
|---|---|
| 0–3 months | Responds to sounds and bright lights; reacts to touch |
| 4–6 months | Begins grasping objects, tracking movement, shows taste preferences |
| 7–9 months | Develops color vision, responds to name, explores with mouth and hands |
| 10–12 months | Understands basic words, improves coordination and sensory response |
Sight
Initially, infants can only see about 12 inches and recognize bright colors. By 2 months, they begin tracking objects and making head movements. Full color vision and clarity develop by 3–4 months, and sight becomes adult-like between 7–9 months.
📣 Multi-Sensory Learning: Toys that engage multiple senses simultaneously accelerate development. Our Grippies Shakers ($35-$50) combine tactile grip textures with auditory feedback—perfect for 6-18 month olds building sensory connections.
Why it works: Babies learn faster when touch and sound combine. The magnetic connections provide instant tactile and auditory feedback, reinforcing cause-effect understanding.
Hearing
Fully developed at birth — babies recognize familiar voices like their mother's. By 2 months, they start making sounds. By 4 months, they respond to tone. Around 6–7 months, they mimic sounds and start understanding basic speech.
🔊 Auditory Development Tool: Our Montessori Sound Cylinders ($45-$60) help toddlers ages 2-6 discriminate between different sounds and volumes—a key skill for language development and auditory processing.
How to use: Children shake each cylinder to match pairs by sound. This trains the ear to detect subtle differences—essential for phonics and reading readiness. Start with 3 pairs, expand to 6 as skills improve.
Taste
Fully developed at birth. Babies can differentiate sweet, sour, bitter, and bland, and may reject certain foods based on taste or texture.
Why Is Sensory Development Significant?
The five senses allow humans to be aware of their bodies and surroundings in order to function and perform daily tasks. They also play a crucial role in physical, social, and cognitive development.
- The sense of touch supports fine motor development (e.g., pincer grasp).
- Check out our collection of Montessori toys that promote fine motor skills to support this important stage of development.
- Sensory input helps children identify hot/cold or soft/rough objects.
- Hearing, sight, and touch assist in developing social skills through interaction and communication.
🎨 Top 5 Sensory Development Toys: Side-by-Side Comparison
Not sure which sensory toy is right for your child's stage? Here's a quick comparison of our most effective sensory development tools:
| Toy | Age Range | Senses Engaged | Skills Developed | Price | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sound Cylinders | 2-6 years | Hearing, Touch | Auditory discrimination, listening skills, pattern recognition | $45-$60 | Children developing language skills or needing auditory focus training |
| Sensory Table | 18mo-5yrs | Touch, Sight, Hearing | Fine motor, sensory exploration, imaginative play, hand-eye coordination | $80-$120 | Creating dedicated sensory play station for messy materials (rice, water, sand) |
| Grippies Shakers | 6mo-3yrs | Touch, Hearing, Sight | Tactile feedback, auditory response, grip strength, cause-effect understanding | $35-$50 | Babies and toddlers exploring textures and sounds simultaneously |
| Sorting Toys | 18mo-5yrs | Touch, Sight | Visual discrimination, tactile differentiation, problem-solving, color/shape recognition | $35-$99 | Children learning to categorize and match by visual and tactile cues |
| Name Trains | 2-6 years | Touch, Sight | Tactile letter recognition, visual letter identification, fine motor, spelling | $30-$80 | Multi-sensory letter learning through touch and sight combined |
💡 Pro Tip: Combine multiple sensory toys for comprehensive development. For example, use Sound Cylinders for auditory training, then transition to Name Trains for tactile letter practice—engaging hearing first, then touch and sight together.
🌟 Our Top 3 Sensory Development Tools (Ages 6mo-6yrs)
Support your child's sensory growth with hands-on Montessori materials designed for multi-sensory exploration. Each tool targets specific developmental needs:
Sensory Play Activities to Improve Development
Sensory play activities are key to developing sensory awareness. These activities include:
- Playing in the sandbox
- Playing with Play-Doh
- Creating and using string phones
- Walking barefoot on different surfaces like grass, sand, and concrete
- Making collages with varied materials
🎨 Create a Dedicated Sensory Station
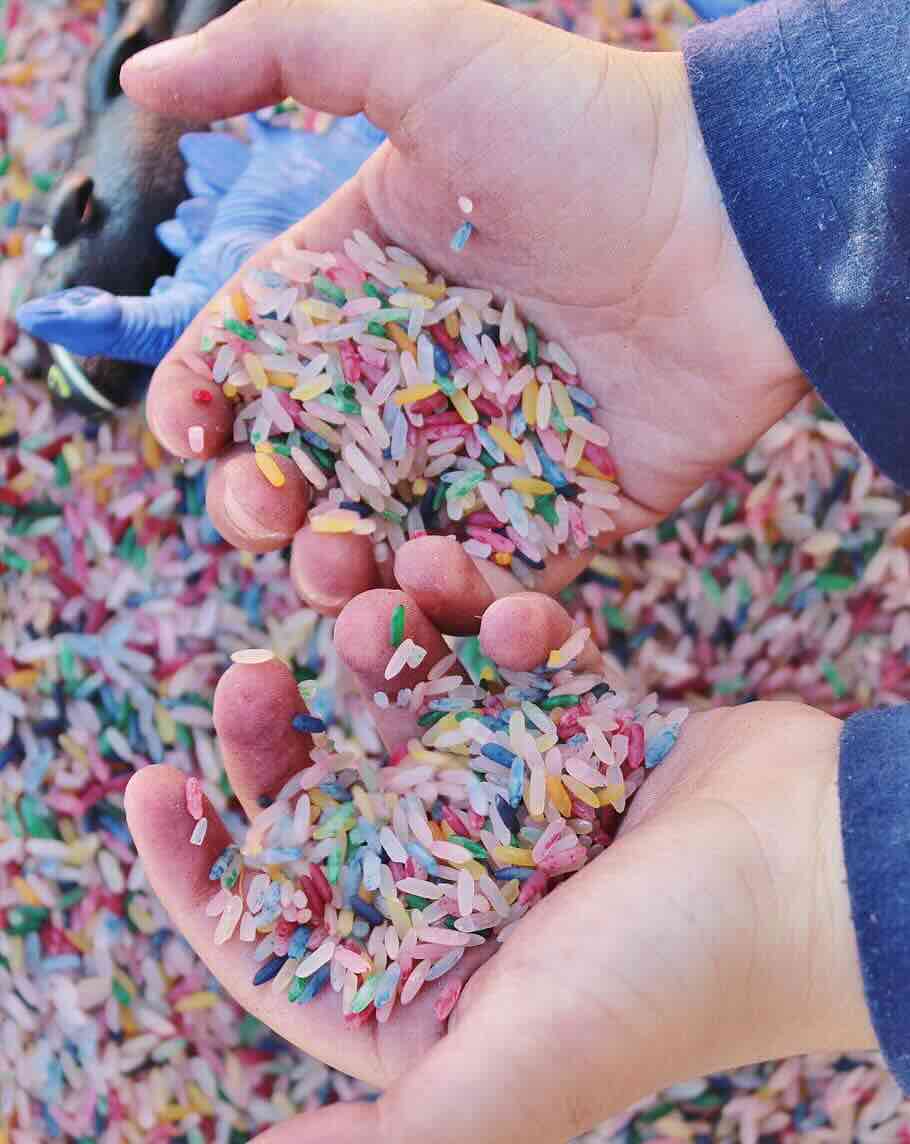
Instead of scattered sensory activities, create a permanent sensory exploration area with our Toddler Sensory Table ($80-$120)—the single best investment for multi-sensory development.
Weekly rotation schedule:
- Week 1: Rice + measuring cups (touch, sight, hearing)
- Week 2: Water + funnels (touch, sight, cause-effect)
- Week 3: Sand + small toys (tactile exploration)
- Week 4: Beans + sorting containers (fine motor, sorting)
Why parents love it: Contains mess in one area, children stay engaged for 30+ minutes, and cleanup takes 2 minutes. See sensory table →

The sensory development process follows a natural rhythm. Engaging with children through play enhances their ability to process and respond to sensory input in their environment.
Common Sensory Processing Disorders in Children
Delayed or irregular sensory development may indicate a sensory disorder. Common types include:
- Sensory Discrimination Disorder: Difficulty distinguishing stimuli by sight, sound, taste, or smell.
- Sensory-Based Motor Skills Disorder: Delays in movement, posture, or coordination due to poor sensory input processing.
- Sensory Modulation Disorder: Overreaction or underreaction to environmental stimuli.
Early Signs of Sensory Disorders
- Overreacting to sounds, lights, or touch
- Difficulty with coordination (e.g., tripping, bumping into things)
- Avoiding certain textures (clothes, food, materials)
- Craving intense sensory experiences (spinning, crashing)
- Trouble focusing or regulating emotions in noisy environments
If your child consistently displays intense sensitivity, withdrawal, or difficulties in motor skills, consult a pediatrician or occupational therapist specializing in sensory integration.
For more information on sensory processing disorders in children, check outNational Library of Medicine.
💌 Early Intervention Through Play
Occupational therapists often recommend structured sensory play for children with processing challenges. Tools like sound discrimination toys ($45-$60) and dedicated sensory stations ($80-$120) provide controlled sensory input in a safe environment.
Common OT recommendations:
- Sound Cylinders for children with auditory processing delays
- Sensory Tables for children who seek tactile input
- Sorting Toys for visual discrimination challenges
Always consult with your child's occupational therapist before implementing sensory activities for diagnosed disorders.
Conclusion
Sensory development is a foundational part of childhood growth. Caregivers should observe their children closely and encourage sensory activities that support healthy development.
Works Cited
Dictionary.cambridge.org. 2021. sense. [online] Available here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the five sensory skills?
The five sensory skills are sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. These senses help children understand and interact with the world around them.
How do you help a child with sensory issues?
Start with simple sensory play activities like sandbox play, finger painting, or walking on different textures. Avoid overstimulation and observe your child’s reactions to understand what supports or overwhelms them.
Can sensory development affect learning?
Yes. Sensory development plays a crucial role in building cognitive skills, coordination, language, and emotional regulation—especially in early childhood.
We’d Love to Hear From You!
Have you noticed changes in your child’s senses as they grow? What kinds of sensory play do your kids love most? Share your experience in the comments below — your story might help another parent!
Support Your Child's Sensory Development
Shop our educator-approved Montessori sensory materials
Free U.S. Shipping • Quality Guaranteed • Montessori-Approved








